Blood group systems are a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of antigens on the surface of red blood cells. An antigen is a molecule that can stimulate an immune response (antibody production).
Types:
ABO Blood Group
A positive(+)
A negative(-)
B positive(+)
B negative(-)
AB positive(+)
Ab negative(-)
O positive(+)
O negative(-)
ABO Blood Groups:
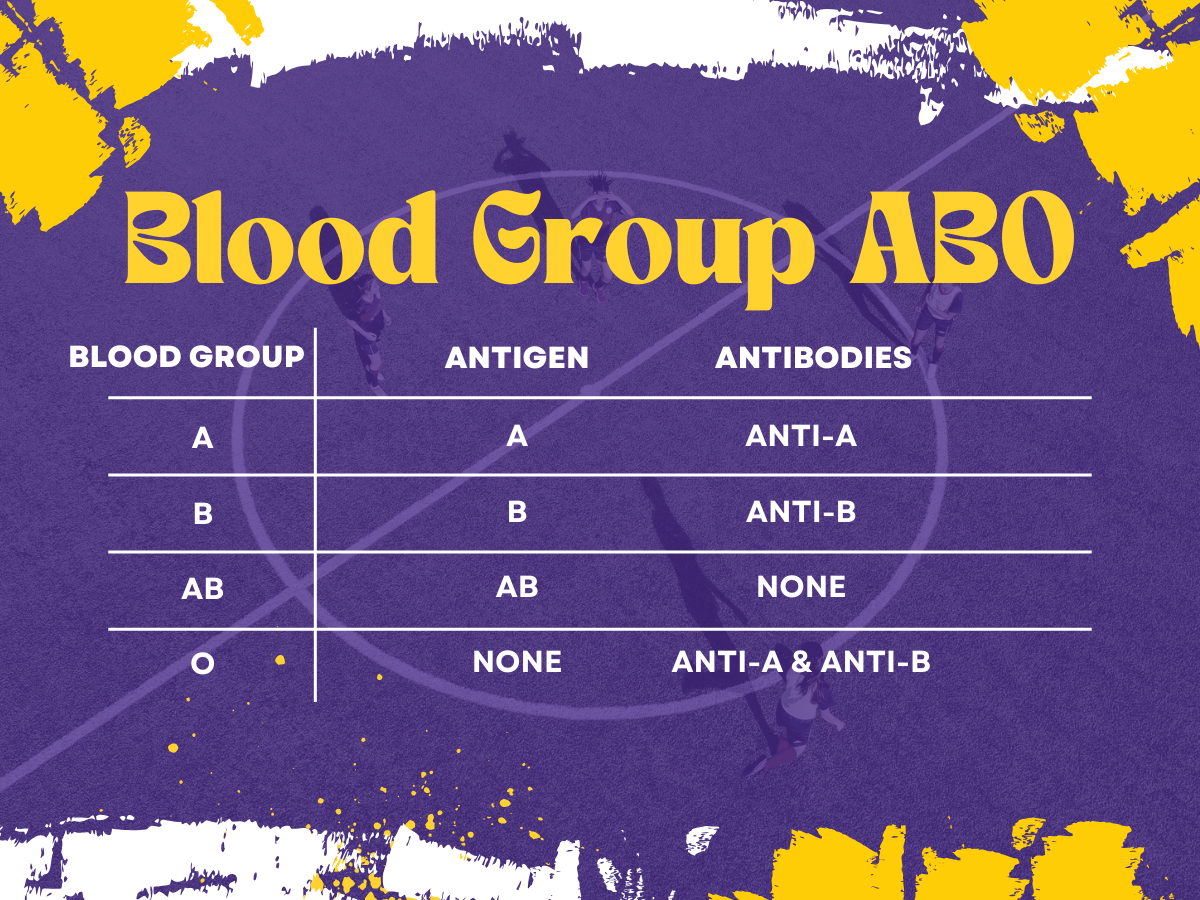
It is the most important blood group system in humans. Austerian scientist Karl Landsteiner first discovered the ABO blood group system. In this system, there are four different blood groups distinct from each other on the basis of specific antigens (antigens A and B) present on the surface of Red Blood Cells. In a person, antigen A has blood group A, Similarly a person having antigen B has Blood Group B, and A person having antigen AB both then its blood group is AB, When a person’s blood has no antigen its blood group is O.
When a child is born, 2 types of antibodies anti-A and anti-B antibodies appear in the blood serum of that child. The presence of these antibodies depends on the corresponding antibodies present in the blood. In a person with blood group A, antigen A is present and antigen B is absent. Their blood will contain anti-B antibodies. In a person with blood group B, antigen B is present and A is absent. So they will contain anti-A antibodies. In a person having blood group AB, both antigens are present A&B. Neither is absent. Their blood contains no antibodies. In a person with blood O, neither antigen A nor antigen B is present. In his blood group, both antigens are absent. So their blood serum contains both anti-A and anti-B antibodies.
Blood Transfusion in ABO Blood Group System:
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood or blood-based products from one person into the circulatory system of another. Blood transfusion is life-saving in some situations, such as massive blood loss due to injury, or can be used to replace blood lost during anemia, hemophilia, thalassemia or suckle cell diseases may require frequent blood transfusions.
Transfusion of blood is done after confirming that no agglutination(clumping of cells) results in the blood of the recipient. If agglutination occurs, the clumped cells do not pass easily through capillaries and block the capillaries. For the confirmation of no agglutination, blood samples of the donor and recipient are cross-matched for compatibility. Anti-bodies of the recipient’s blood may destroy the corresponding antigen containing the Red Blood Cells of the donor or antibodies of the donor’s blood may destroy the antigen containing the Red Blood Cells of the recipient. O blood group individuals are called universal donors because they can donate blood to the recipients of every other blood group. AB blood group individuals are called universal accepters because they can receive transfusions from the donors of every other blood group.
Rh blood group system +ve or -ve:
In 1930 Karl Landsteiner discovered the Rh blood group system. In this system are two blood groups Rh positive and Rh negative. These blood groups are distinct from each other on the basis of antigens called Rh factors. Rh factors were first discovered in Rhesus monkeys. A person having Rh factors has a positive blood group. If a person has no Rh factors then its blood group is Rh-negative.
Unlike the naturally occurring anti-A and anti-B antibodies of the ABO system, an Rh-negative person does not produce anti-Rh antibodies unless the Rh factor enters his/her blood.
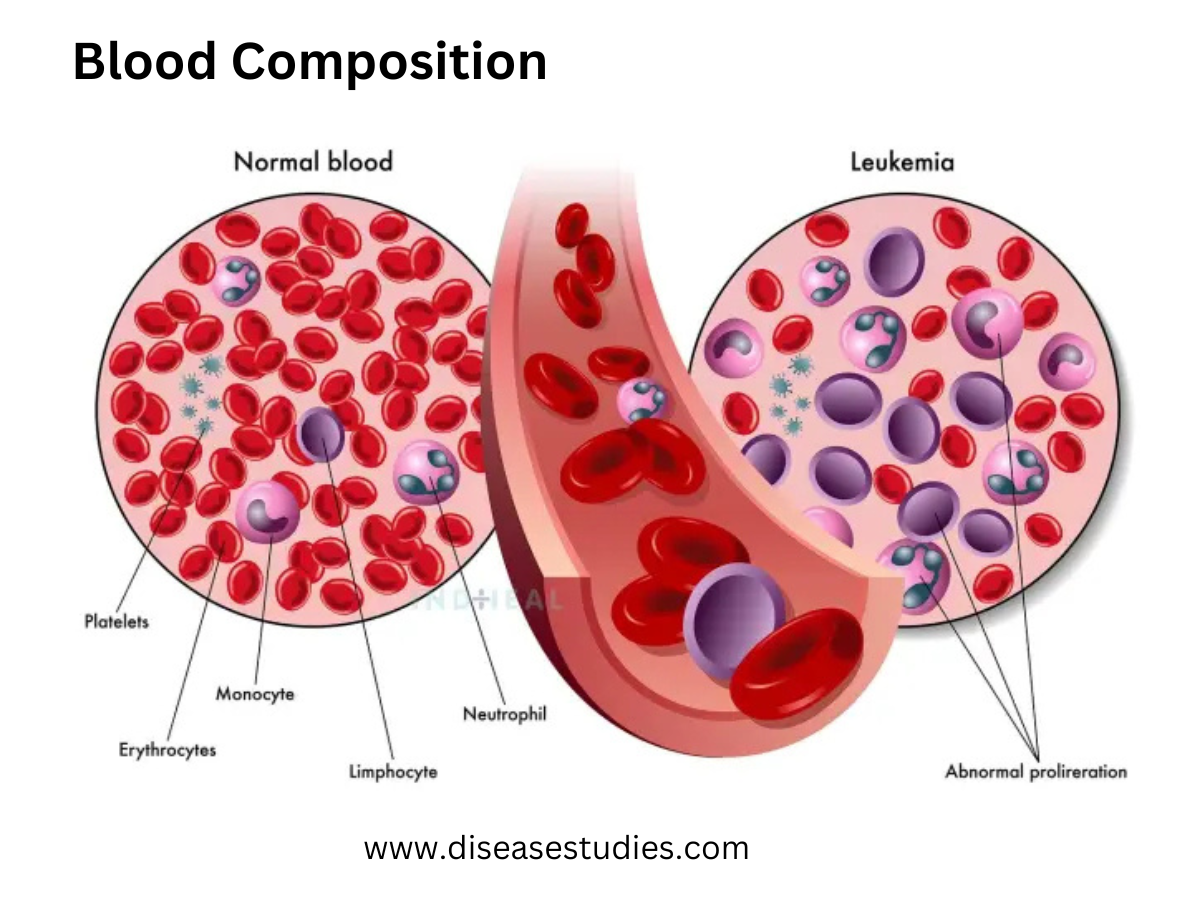
Blood Cancer:
Blood cancer is a disease that includes leukemia, bleeding disorders, and thalassemia. A change in DNA genes commonly causes blood cancer.
Types of Blood Cancer:
Leukemia:
Leukemia is the production of many immature and abnormal white blood cells. This is caused by a cancerous mutation (change in gene) in bone marrow or lymph tissue cells. It is a serious disorder, and the patient needs to change the blood regularly with normal blood. (got from donors) It can be cured by bone marrow or lymph tissue cells. It is a dire situation and is a very costly treatment.
Thalassemia:
It is caused by a change in the gene of hemoglobin. This change results in defective hemoglobin being produced and the patient cannot transport oxygen properly. With normal blood, the blood of this patient is replaced regularly. It can be cured by bone marrow transplant but it does not give a 100% cure rate.
World Thalassemia Day:
The International Thalassemia is celebrated on 8th May Every Year. This day is dedicated to raise public awareness about thalassaemia and to highlight the importance of the care for thalassaemia patients.



218GB PRIVATE Amateur Videos MAGNET TORRENT DOWNLOAD
CHILDREN PORN FREE VIDEO HENTAI INZEST DARKNET SITES
218GB MAGNET LINK FOR TORRENT CLIENT (ADD URL) magnet:?xt=urn:btih:abd5aaed52b5994fe54136701c4c18156bd28415
ВЕБСАЙТ: ОТКРЫВАЙТЕ ТОЛЬКО В АНОНИМНОМ ТОР БРАУЗЕРЕ, ССЫЛКА http://torx5mtxatfovjmdizm27tsqusa4bgej5qx7zvv2quxvh44spl5xzsad.onion
Лучшее архитектурное бюро в СПб — воплощаем в жизнь ваши архитектурные мечты
архитектурное бюро спб http://proektnoe-byuro.ru/ .
Профессиональные штопоры и открывалки — удобные решения для безупречного открытия вина
открывалка для бутылок http://www.vseodlyakuhni.ru/ .
Финки НКВД — легендарные ножи для коллекции и повседневного использования
финка нож https://nozhiforall.ru .
Керамические тарелки для стильного ужина — сделайте обеды особенными
бульонные пары http://www.posudaklub.ru .
Прочные и стильные френч-прессы — наслаждайтесь вкусом свежего кофе каждый день
кофейники френч пресс https://www.posudakitchen.ru .
Наркологическая помощь при запое в Самаре — вывод из запоя с гарантией безопасности
вывод из запоя недорого https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rehab.ru/ .
Купить опасную бритву с доставкой — идеальный инструмент для гладкого бритья
опасная бритва цена https://pro-nozhi.ru .
Почему лизинг коммерческого транспорта так популярен
лизинг коммерческих автомобилей для ип kommercheskij-transport-v-lizing-1.ru .
Удобные кувшины для холодных напитков — идеальные для летних вечеринок
кувшин 1 л http://www.elitenposuda.ru .
Юнистим: инновации в производстве нефтегазовой и строительной спецтехники
завод по производству спецтехники unisteam com
Немецкие маникюрные наборы Solingen — стиль и надежность для вашего маникюра
solingen маникюрный набор купить https://www.nozh-kitchen.ru/ .
Туристические ножи для выживания и походов — универсальные инструменты с доставкой
туристический нож купить https://klubnozhey.ru .
Услуги профессионального сантехника в СПб: доступные цены, гарантия качества и оперативный выезд
услуги сантехника цена http://ceny-na-uslugi-santehnika.ru/ .
Сантехник в СПб: монтаж водопроводных систем, установка сантехники и оперативный ремонт по низким ценам
расценки на сантехнические работы в санкт петербурге расценки на сантехнические работы в санкт петербурге .
Где найти опытного сантехника в Санкт-Петербурге? Цены на услуги по установке и ремонту сантехники
услуги сантехника цены https://www.ceny-na-santehnicheskie-uslugi.ru .
Пропуск на МКАД для грузовых автомобилей: как избежать штрафов за отсутствие разрешения
сделать пропуск на мкад http://www.propuskamos1.ru .
Цифровое телевидение Уфанет: более 200 каналов для всей семьи
уфанет уфа цены http://www.ufanet-oficialnyy-sayt.ru .
Мегапласт: производство упаковочной пленки для всех типов продукции
мегапласт ооо megaplast24 ru
Вывод из запоя в Самаре: врач нарколог готов помочь 24/7
частный вывод из запоя http://www.vivod-iz-zapoya-samare.ru/ .
Завод по изготовлению винтовых свай: лучшие предложения на рынке строительных материалов
завод винтовых свай москва zavod-vintovyx-svaj.ru .
Как быстро и безопасно выйти из запоя в Самаре? Вызов нарколога
вывести из запоя самара https://www.vivod-iz-zapoya-samarskiy.ru .
Как замаскировать септик? Декоративные камни от компании Декор Септиков
искусственный камень декоративный на колодец dekorseptikov com
Интернет-эквайринг для сайта: быстрое подключение и простая настройка
интернет эквайринг для ооо интернет эквайринг для ооо .
Жалюзи и рулонные шторы для любого интерьера: стильные решения от производителя
кассетные рулонные шторы http://www.rulonniye-shtori.ru .
Где купить грузоблочный тренажер? Лучшие предложения для тренировок
грузоблочный тренажер для ног https://www.gruzoblochnij-trenazher.ru .
Анонимное лечение в наркологической клинике: полная конфиденциальность и профессионализм
наркологический центр в спб https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-spb1.ru/ .
Клиника психиатрии в Санкт-Петербурге: помощь при депрессии, стрессах и тревоге
частная психиатрическая больница http://psihiatricheskaya-klinika-spb.ru/ .
vsehdiplom ru: профессиональные услуги по написанию дипломов и курсовых
Словосочетания http://www.vsehdiplom.ru/blog/lajfhaki-po-russkomu-jazyku-razbiraemsja-s-chastjami-rechi/ .
Продажа бытовок для строительных нужд: надежные и качественные решения
бытовки bytovki-moskva01.ru .
Купить экран для проектора: широкий ассортимент моделей с доставкой по России
экран проекционный http://www.ehkrany-dlya-proektorov01.ru .
Каркасные дома под ключ: качественное строительство и доступные цены
каркасник под ключ каркасник под ключ .
Почему каркасный дом — лучшее решение для дачи и постоянного проживания
каркасный дом в спб http://karkasnye-doma-pod-klyuch-v-spb.ru/ .
Купить металлопрокат на siburalmet ru: доступные цены и гарантированное качество
СибУрал Металл – металлопрокат Омск siburalmet ru
Сколько стоит проектирование: Узнайте цены и этапы работ
проектные работы в строительстве цена http://proektnye-raboty-cena.ru/ .
Quick and Easy Stamp Maker for Custom Rubber Stamps
stamp maker http://stamps-maker-online.com .
Как выбрать металлопрокат? Советы от металлобазы АльфаСтройМет
АльфаСтройМет – металлобаза Махачкала
Online Stamp Maker for Custom Stamps: Reliable and Fast Delivery
online stamp maker https://www.stamp-creator-online.com .
Продажа электропогрузчиков для любых задач: надежность и эффективность
электропогрузчик вилочный https://www.xn—1-glchlgldd6aalleyw3e1e.xn--p1ai .
Металлобаза КА-Металл предлагает металлопрокат для любых задач. Оформите заказ с доставкой на kametall ru.
КА-Металл – металлобаза Славянск-на-Кубани kametall ru
Продажа электропогрузчиков для складов и производственных помещений
вилочные погрузчики электрические http://xn—1-glchlgldd6aalleyw3e1e.xn--p1ai/ .
Металлобаза Юметалл предлагает широкий выбор качественного металлопроката для строительства и производства. Надежные материалы, выгодные цены и быстрая доставка по всей России.
Юметалл – металлобаза Тобольск
Лизинг грузовых автомобилей: удобный способ обновить автопарк
грузовики в лизинг http://www.gruzovye-avtomobili-v-lizing.ru/ .
Оклейка авто винилом для долгосрочной защиты и уникального дизайна
оклейка капота пленкой okleyka-avto-plenkoy-1.ru .
Лизинг оборудования: обновляйте технику и развивайте бизнес
оборудование лизинг http://www.oborudovanie-v-lizing.ru/ .
Каркасный дом с террасой: проекты для комфортной загородной жизни
строительство каркасных домов спб spb-karkasnye-doma.ru .
Как сдавать спермограмму в СПб: полное руководство по подготовке и проведению анализа
сдача спермограммы спб http://www.eggdonorsspb.ru .
ЭКО по ОМС в СПб: как воспользоваться государственной программой
эко по омс в спб как получить квоту https://www.embryoscopespb.ru/ .
Центр репродуктологии в СПб: как современные методы лечения бесплодия помогают сотням пар
клиника эко спб http://reproductologyonline.ru/ .
Запчасти ВАЗ: экономьте время и деньги, заказывая в удобном онлайн-каталоге
магазин запчастей ваз http://www.zapchasti-vaz01.ru/ .
ЛАДА деталь: лучшие цены на оригинальные и совместимые запчасти для ВАЗ
лада деталь каталог и цены http://www.zapchasti-vaz-01.ru/ .
Каркасные дома под ключ: энергоэффективные технологии для круглогодичного проживания
каркасные дома одноэтажные https://www.karkasnye-doma-pod-klyuch-msk1.ru/odnoetazhnye .
Stamp Maker Online: Simplify Your Branding with Personalized Stamps
free stamp maker online https://www.stamp-online-maker.com .
Готовые модульные дома с отделкой и подключением коммуникаций для вашего участка
модульные дома под ключ круглогодичного проживания https://modul-stroy-spb.ru .
Современные каркасные дома для жизни за городом с высоким комфортом
каркасные дома спб http://www.spb-karkasnye-doma1.ru .
Каркасный дом под ключ: сочетание современных технологий и комфортной жизни
дома каркасные http://karkasnyi-dom-pod-klyuch-1.ru/ .
Мобильные экраны для проекторов: удобное решение для презентаций
проекционный экран для проектора http://www.ehkrany-dlya-proektorov0.ru/ .
Микрозаймы без отказа для людей с любой кредитной историей: простые условия
займ срочно без отказа https://www.dengikg.ru/ .
Выбор недорогого сервера HP Proliant, Индивидуальный подход к выбору сервера HP Proliant
сервер делл купить http://www.servera-hp-proliant.ru .
Ипотека в Бишкеке для семей: доступное жильё с минимальными платежами
ипотекав Бишкеке https://ipotekakg.ru/ .
Казино Клубника: как начать и успешно играть в онлайн-игры
клубника казино клубника казино .
Септик для загородного дома: удобное решение для автономной канализации
септики https://www.septik-pod-kluch-moskwa.ru/ .
Online Stamp Maker for Quick and Easy Custom Stamp Solutions
stamp maker online https://www.stampingandblogging.com .
Безопасный вывод из запоя в Самаре: доверьтесь опытным наркологам
вывод из запоя цена вывод из запоя цена .
Design and Order Rubber Stamps Online in Just Minutes
stamp making online stamp making online .
Пропуск на МКАД для бизнеса: минимизируйте затраты времени и денег
пропуска на грузовые машины в москве пропуска на грузовые машины в москве .
Оптимальные серверы HP для малого бизнеса
купить серверы hp https://kupit-server-hp.ru .
Опытный сантехник для сложных задач: от ремонта до монтажа систем водоснабжения
услуги сантехника в спб http://www.vyzov-santeh-nik-spb.ru/ .
Пропуск на МКАД для грузовых машин: оформляем быстро и надёжно
пропуск на мкад для грузовых машин цена https://www.propusknamkad111.ru .
Срочный ремонт от опытных сантехников в Сан-Хосе!, Экстренный вызов сантехника в Сан-Хосе.
Эффективный ремонт сантехники по доступной цене, Звоните прямо сейчас для записи на удобное время.
Решаем любые проблемы с водопроводом в Сан-Хосе, Гарантированное качество услуг по ремонту сантехники.
Эксперт по установке душевых кабин в вашем районе, Профессиональный подход к любой задаче в сфере сантехники.
Качественный ремонт труб в Сан-Хосе любой сложности, Оставьте заявку на ремонт сантехники и мы свяжемся с вами.
Эффективный ремонт канализации по доступной цене, Мы гарантируем профессиональный подход и быстрое выполнение работы.
Нужен ремонт сантехники в Сан-Хосе? Мы вам поможем!, Быстрое решение любых проблем с водопроводом.
plumber san jose http://plumbersan-joseca4.com .
Кашированная фольга для упаковки: стильное и надёжное решение
кашированная фольга для шоколада http://www.ufalaki.ru/ .
Монтаж систем тёплого пола: услуги сантехника для вашего дома
вызов сантехника спб http://www.vyzov-santehnika-spb-52.ru/ .
Лизинг грузовых машин: минимальный первый взнос и комфортные условия
грузовой автомобиль в лизинг http://www.gruzovye-avtomobili-v-lizing1.ru/ .
Септики под ключ: профессиональная помощь в установке автономных систем
септики под ключ https://septik-pod-klych-99.ru .
Обслуживание септиков: профессиональная помощь в любое время
септик цена [url=https://www.septik-pod-kluch-moskwa.ru/]https://www.septik-pod-kluch-moskwa.ru/[/url] .
Услуги профессионального сантехника: ваш комфорт — наша работа
сантехник спб [url=https://vyzov-santeh-nik-spb.ru/]https://vyzov-santeh-nik-spb.ru/[/url] .
Комплексные услуги по монтажу септика под ключ с гарантией
септики под ключ [url=https://www.septic-pod-kluch-msk.ru/]https://www.septic-pod-kluch-msk.ru/[/url] .
Прыжки с парашютом: сделайте шаг к незабываемым впечатлениям
прыгнуть с парашютом [url=https://pryzhki-s-parashyutom-v-spb.ru]https://pryzhki-s-parashyutom-v-spb.ru[/url] .
Лечение зубов у детей в Архангельске: забота о здоровье с самого раннего возраста
стоматологический кабинет [url=http://www.dentalstudio-29.ru/]http://www.dentalstudio-29.ru/[/url] .
Кашированная фольга для упаковки: стильное и надёжное решение
фольга упаковка [url=ufalaki.ru]ufalaki.ru[/url] .
Сантехник на дом: монтаж унитазов и установка инсталляций
вызвать сантехника [url=vyzov-santehnika-spb-52.ru]vyzov-santehnika-spb-52.ru[/url] .
Иновативни сглобяеми къщи: съчетавайте модерен стил и функционалност
цени на сглобяеми къщи [url=https://sglobyaemi-kushti.com]https://sglobyaemi-kushti.com[/url] .
Интернет-магазин шин: покупка резины онлайн с минимальными усилиями
интернет магазин шин с доставкой [url=https://www.shiny-internet-magazin.ru/]https://www.shiny-internet-magazin.ru/[/url] .
продвижение в социальных сетях стоимость
Оформление пропусков на МКАД для грузовиков: экономьте время
пропуск для грузовых машин цена [url=https://propusknamkad111.ru/]пропуск для грузовых машин цена[/url] .
Интернет-магазин шин: покупайте шины выгодно с доставкой на дом
купить авторезину [url=http://kupit-shiny-spb.ru/]http://kupit-shiny-spb.ru/[/url] .
Каталог запчастей ВАЗ: выбирайте детали по модели вашего авто
оригинальные запчасти ваз [url=https://www.avtozapchasti-vaz1.ru/]https://www.avtozapchasti-vaz1.ru/[/url] .
Лизинг грузовых автомобилей с гарантией: качественные услуги и выгодные условия
купить в лизинг грузовой автомобиль [url=https://www.lizing-gruzovyh-avto.ru]https://www.lizing-gruzovyh-avto.ru[/url] .
Постройте каркасный дом мечты с гарантией качества и долговечности
каркасные дома под ключ проекты и цены [url=https://karkasnye-doma-v-spb-pod-kluch.ru/]каркасные дома под ключ проекты и цены[/url] .
Стоматология Архангельск: профессиональное протезирование зубов
врач стоматолог архангельск [url=http://dentalstudio-29.ru/]http://dentalstudio-29.ru/[/url] .
Современные септики под ключ: установка и обслуживание в одном месте
септик цена с установкой под ключ [url=http://www.septik-pod-klych-99.ru/]http://www.septik-pod-klych-99.ru/[/url] .
Установка септиков под ключ: профессиональные услуги в вашем регионе
сколько стоит септик под ключ [url=http://septic-pod-kluch-msk.ru/]http://septic-pod-kluch-msk.ru/[/url] .
Преимущества каркасного дома: доступность, скорость и энергоэффективность
каркасный дом [url=http://www.karkasnye-doma-v-spb-1.ru/]http://www.karkasnye-doma-v-spb-1.ru/[/url] .
Деревянный дом под ключ: строим быстро и с гарантией качества
дом деревянный под ключ цена [url=https://derevyannye-doma-pod-klyuch777.ru]https://derevyannye-doma-pod-klyuch777.ru[/url] .
Ваш лучший опыт: прыжки с парашютом с профессионалами аэроклуба
прыжки с парашютом в санкт петербурге цены [url=https://www.pryzhki-s-parashyutom-v-spb.ru/]https://www.pryzhki-s-parashyutom-v-spb.ru/[/url] .
Как оформить грузовой автомобиль в лизинг за один день?
лизинг грузовых автомобилей для юридических лиц [url=http://www.gruzovye-avtomobili-v-lizing1.ru]http://www.gruzovye-avtomobili-v-lizing1.ru[/url] .
Как узнать стоимость проектирования: Консультации и расчёты бесплатно
стоимость проектирования за м2 [url=https://proektnye-raboty-ceny1.ru/]https://proektnye-raboty-ceny1.ru/[/url] .
Каркасные дома для больших семей: просторные проекты с мансардой
каркасный дом санкт петербург [url=https://www.karkasnye-doma-v-spb178.ru]https://www.karkasnye-doma-v-spb178.ru[/url] .
Каркасные дома под ключ: индивидуальные проекты по выгодным ценам
дома каркасные спб [url=https://karkasnye-doma-v-spb-pod-kluch1.ru]https://karkasnye-doma-v-spb-pod-kluch1.ru[/url] .
Септики под ключ: профессиональная помощь в установке автономных систем
септик с установкой под ключ [url=http://septik-pod-klych-99.ru/]http://septik-pod-klych-99.ru/[/url] .
Вашият нов дом за няколко седмици: модерни сглобяеми къщи
сглобяеми къщи цена [url=https://sglobyaemi-kushti.com/]сглобяеми къщи цена[/url] .
Выгодный лизинг грузового транспорта: экономия и удобство
грузовой транспорт в лизинг [url=http://lizing-gruzovyh-avto.ru/]http://lizing-gruzovyh-avto.ru/[/url] .
Ваш лучший опыт: прыжки с парашютом с профессиональными инструкторами
прыжок парашютом цена [url=https://pryzhki-s-parashyutom-v-spb.ru/]прыжок парашютом цена[/url] .
Find the top online schools in Wisconsin, with detailed rankings and reviews.
Join a prestigious online school in Wisconsin, to kickstart your learning experience.
Take classes online from the convenience of your Wisconsin home, with flexible schedules and personalized support.
Enhance your career prospects with an online degree in Wisconsin, from reputable online colleges in Wisconsin.
Realize your educational aspirations with an online program in Wisconsin, designed to meet your requirements and timetable.
Connect with fellow students in virtual classrooms in Wisconsin, and create valuable connections for your career.
Access resources and materials online for your courses in Wisconsin, to excel in your online education and succeed in your online school.
Online Schools in Wisconsin [url=http://onlineschoolwi6.com]http://onlineschoolwi6.com[/url] .
Объемные наклейки: акцент на вашем продукте или услуге
наклейки со смолой [url=https://xn—–7kcbbyacb2akkclkqcl8a3dxf3b0a4b.xn--p1ai/]наклейки со смолой[/url] .
Лечение алкоголизма в наркологической клинике СПб: гарантия результата
наркологический центр санкт петербург [url=narkologicheskaya-klinika-spb-1.ru]narkologicheskaya-klinika-spb-1.ru[/url] .
Индивидуальные программы лечения в наркологической клинике
наркологическая клиника спб [url=https://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-spb-0.ru/]https://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-spb-0.ru/[/url] .
Каркасные дома с современным дизайном и функциональной планировкой
каркасный дом [url=https://karkasnye-doma-v-spb-1.ru/]каркасный дом[/url] .
Каркасный дом на 100 кв.м.: комфортное жилье для вашей семьи
каркасные дома под ключ проекты и цены [url=http://karkasnye-doma-v-spb-pod-kluch.ru/]http://karkasnye-doma-v-spb-pod-kluch.ru/[/url] .
Экологически чистые деревянные дома под ключ: комфорт круглый год
строительство деревянных домов москва [url=derevyannye-doma-pod-klyuch777.ru]derevyannye-doma-pod-klyuch777.ru[/url] .
Сглобяеми къщи с гарантирано качество: комфортен дом за кратко време
къщи сглобяеми [url=https://sglobyaemi-kushti.com/]https://sglobyaemi-kushti.com/[/url] .
Казино Клубника: топовые джекпоты и бонусы ждут вас
казино клубника [url=http://goo.su/rcfb/]http://goo.su/rcfb/[/url] .
Модели камер заднего вида для грузовиков с антибликовым покрытием
камера заднего вида 24в для грузовиков [url=http://kamera-dlya-gruzovika.ru/]http://kamera-dlya-gruzovika.ru/[/url] .
Наклейки со смолой с эффектом объёма: современное решение для бизнеса
стикеры со смолой [url=https://www.xn—–7kcbbyacb2akkclkqcl8a3dxf3b0a4b.xn--p1ai/]https://www.xn—–7kcbbyacb2akkclkqcl8a3dxf3b0a4b.xn--p1ai/[/url] .
Магазин шин: лучшие бренды резины для вашего автомобиля
шины магазин [url=http://shiny-internet-magazin.ru/]http://shiny-internet-magazin.ru/[/url] .
Лучшие условия кредита на карту в банках вашего города
кредит на карту без отказа бишкек [url=http://www.kreditkg.ru/]http://www.kreditkg.ru/[/url] .
Discover the top online schools in Missouri, providing flexible learning options.
Start your online education journey in Missouri, that guarantees a high-quality education.
Considering online schools in Missouri for your next academic venture?, Browse through our top picks.
Obtain a quality education online in Missouri, with engaging course materials.
What are the benefits of online education in Missouri?, Learn about the opportunities available.
Join a supportive online community in Missouri, to collaborate on projects.
Access the digital library of online educational institutions in Missouri, to enhance your studies.
Online Schools in Missouri [url=http://www.onlineschoolmo6.com]http://www.onlineschoolmo6.com[/url] .
Explore the best online schools in Utah, from the comfort of your home.
Join a prestigious online school in Utah, to kickstart your academic career.
Earn your diploma remotely in Utah, with convenient classes and top-notch professors.
Engage in discussions with peers in online schools in Utah, and build your network for the future.
Participate in hands-on activities in online schools in Utah, to enhance your learning experience and retention.
Benefit from academic guidance in Utah online schools, to support your academic journey.
Pick the perfect major in online schools in Utah, that align with your passions and aspirations.
Progress in your academic journey with online schools in Utah, for a successful and fulfilling career.
Online Schools in Utah [url=http://onlineschoolut6.com]http://onlineschoolut6.com[/url] .
Высокотехнологичное производство спецтехники для вашего бизнеса
продажа грузовой спецтехники [url=https://proizvodstvo-spectekhniki.ru/]https://proizvodstvo-spectekhniki.ru/[/url] .
Uncover the advantages of online schools in Louisiana
Online Schools in Louisiana [url=https://www.onlineschoolla8.com/]https://www.onlineschoolla8.com/[/url] .
Экраны для проектора с антибликовым покрытием: максимум чёткости
экраны для проекторов купить [url=https://www.proekcionnye-ehkrany.ru/]https://www.proekcionnye-ehkrany.ru/[/url] .
Интернет для офиса: подключение высокоскоростного доступа за минимальное время
интернет в офис недорого [url=http://www.internet-v-ofis1.ru]http://www.internet-v-ofis1.ru[/url] .
Top Online Schools in Colorado, Get Started with Online Education in Colorado, Choose from the Best Online Schools in Colorado, Explore Online Schools in Colorado, Top-Rated Online Schools in Colorado.
Online Schools in Colorado [url=http://www.onlineschoolco1.com/]http://www.onlineschoolco1.com/[/url] .
Meet singles looking for you. Start connecting today! – https://ugy2mr2.auraflirtsdreams.com/dkf8d6u?m=1
Комплексное мультимедийное оснащение: проекторы, акустика, управление
оснащение мультимедийным оборудованием multimediynoe-osnaschenie1.ru .
Комплексные проекты мультимедийной интеграции для любого бизнеса
интеграция умного аудио с мультимедийными системами интеграция умного аудио с мультимедийными системами .
отели в екатеринбурге
Мы подготовили полезные вопросы для игроков из Казахстана и предложили ответы на них: Промокод ALLUP для ставок в 1xBet.kz. Применение бонусных кодов при регистрации нового аккаунта и на этапе первого пополнения даёт возможность повысить баланс для игры и улучшить стартовые условия
zuvovgveklfob.ru
dako-jobcenter.com
Оборудование для конференц зала: звук, свет, видеосвязь и комфорт
оснащение конференц зала oborudovaniye-konferents-zala1.ru .
Очистка стен от пыли в цеху https://chistka-prom-pomeshchenij-spb.ru/
Уборка паркинга пылесосом https://chistka-parkinga-spb-lo.ru/
Корпоративная электронная почта — это система обмена сообщениями, разработанная для использования организациями и компаниями, которая обеспечивает профессиональную коммуникацию между сотрудниками, клиентами и партнерами. Она включает в себя доменное имя, связанное с компанией, что придает адресам электронной почты официальный вид (например, имя@компания.ru). Подробнее по ссылке https://korp-pochta.ru/
Комплексное оснащение переговорной комнаты: под ключ для вашего удобства
оснащение переговорных комнат под ключ http://www.osnaschenie-peregovornoy-komnaty1.ru/ .
Преди време осъществих пътуване с туристическа агенция Мистрал Травел и останах много удовлетворена! Организацията беше перфектна – от резервацията до самото пътуване. Избрах туристическа програма до Златна Прага и всичко беше организирано на високо ниво – хотелът беше комфортен, екскурзоводът много компетентен, а програмата завладяваща и добре структурирана. Благодарение на тях успях да се насладя на културата и красотата на града без излишни проблеми. С удоволствие бих се използвала услугите на Мистрал за в бъдеще и препоръчвам на всички да изберат техните предложения!
https://www.ukrinformer.com.ua/karta-borodjanki/
Nowe Online Kasyna z Darmowymi Spinami Bez Depozytu. Program bonusowy każdego nowego kasyna online w Polsce obejmuje różnorodne promocje. Użytkownicy mogą je aktywować podczas rejestracji. Są to bonusy pieniężne i darmowe spiny. Pierwsze z nich gracze mogą wydawać według własnego uznania. Drugie, darmowe spiny bez depozytu, można wykorzystać w określonych slotach https://kasynadarmowespiny.pl/
Комплексное оснащение актового зала: инновации для образовательных и культурных мероприятий
оборудование для актового зала купить https://www.oborudovaniye-aktovyh-zalov1.ru/ .
Оснащение ситуационного центра: инновации для управления и принятия решений
оснащение ситуационных центров https://osnascheniye-situatsionnogo-tsentra1.ru/ .
Kasyno Vavada to młode kasyno, które posiada starannie opracowaną platformę, oferującą szeroki wybór automatów do gry od wiodących dostawców. Platforma działa na specjalistycznym rynku od 2017 roku i skierowana jest do graczy z Poland, Ukrainy i innych krajów. Vavada Casino działa legalnie https://vavadas.pl/
Узнайте, где препараты для потенции по выгодной цене прямо сейчас – https://pr-hot1.ru/
https://nspddfgstmqbkl95474.ru/
Ремонт автомобилей по доступным ценам: высокое качество и короткие сроки
partsru.repair remont-avtomobylej.ru .
Мы подготовили важные вопросы игроков Казахстана на тему https://k-arabam.ru/otzivi-i-reyting-1xbet/1xbet-promo-code-free-bet.php и ответы на них. Применение специальных кодов в процессе регистрации и начальном пополнении счёта даёт возможность увеличить сумму на счету и обеспечить выгодный старт игры.
Мультимедийное оснащение: качество, надежность и современные решения
оснащение мультимедийным оборудованием http://www.osnashcheniye-multimediynym-oborudovaniyem1.ru/ .
Мы подготовили для вас основные вопросы для пользователей из Казахстана с детальными объяснениями: Промокоды 1xBet Казахстан для быстрых выигрышей. Применение промокодов во время создания профиля и при первом пополнении баланса открывает шанс обеспечить больше возможностей для игры и создать лучшие условия для начала.
Профессиональная интеграция мультимедийных систем под ключ
интеграция умного аудио с мультимедийными системами https://integratsiya-multimediynykh-sistem1.ru/ .
Find your perfect online school in Oklahoma, check out accreditation and reviews.
Study online at your own pace, take advantage of flexible scheduling.
Embrace the future with distance learning in Oklahoma, thrive in an online school setting.
Choose from a wide range of online schools in Oklahoma, earn your diploma from a respected online school.
Engage in interactive online learning experiences, achieve academic success in a virtual classroom environment.
Take the first step towards your future with a virtual education, realize your dreams through distance learning in Oklahoma.
Online Schools in Oklahoma http://onlineschoolok8.com/ .
Your account is active and growing. Log in now to protect your earnings! – http://extras.byethost4.com/?sid=5166
Принцип эмпатии https://empatiya-intellekt.ru/
Мы разработали полезные советы для казахстанских беттеров с готовыми ответами и советами: https://alina-design.com/doveritelnaya-stavka-i-avansovie-funktsii/1xbet-bonus.php. Активация бонусных кодов при открытии нового счёта и при пополнении счёта в первый раз позволяет расширить стартовые возможности и начать с преимуществами.
Мы собрали полезные вопросы для жителей Казахстана с готовыми ответами: https://mp3hiton.ru/. Применение бонусных кодов во время регистрации и в процессе начального пополнения предоставляет шанс увеличить баланс на счёте и обеспечить выгодный старт игры
Запчасти ВАЗ высокого качества: от мелочей до капитального ремонта
запчасти на ваз https://zapchasti-na-vaz1.ru/ .
Выигрыши в слотах https://casinozanos.ru/
Top Online Schools in Kentucky, Advantages of Online Education in Kentucky, Accredited Online Schools in Kentucky, Discover the Perfect Fit, Online Schools vs Traditional Schools in Kentucky, Cost-Effective Online Schools in Kentucky, Save Money on Tuition, Best Online Middle Schools in Kentucky, Online Elementary Schools in Kentucky, Prepare for Academic Success, Behind the Scenes of Online Schools
Online Schools in Kentucky http://onlineschoolky1.com/ .
мелстрой бонус
Интерактивные панели, акустика и освещение: комплексное оснащение переговорной
оснащение переговорных https://www.osnashcheniye-peregovornoy1.ru/ .
Оснащение и оборудование переговорных комнат под ключ
оснащение переговорных http://www.oborudovaniye-peregovornykh-komnat1.ru .
Креативная сувенирная продукция с логотипом для ваших клиентов
сувенирка с логотипом http://www.suvenirnaya-produktsiya-s-logotipom.ru .
Find Your Perfect Match: Online Schools in New Mexico, Take Your Education to the Next Level with Online Schools in New Mexico, Achieve Your Academic Goals with Online Schools in New Mexico, Empower Your Education with Online Schools in New Mexico, Get Ahead with Online Schools in New Mexico, Embrace the Future of Education with Online Schools in New Mexico, Start Your Online Education Journey in New Mexico, Discover the Benefits of Online Schools in New Mexico, Transform Your Education with Online Schools in New Mexico, Unlock Your Potential with Online Learning in New Mexico
Online Schools in New Mexico https://www.onlineschoolnm3.com/ .
Just thinking about you gives me chills… come closer – https://rb.gy/es66fc?isonge
Почувствуйте азарт с моментальными выплатами выигрышей в 1xBet. Узнайте больше здесь: https://1xbet-zerkalo9.top/
Witamy w Slotico! Tutaj znajdziesz unikalną kolekcję kasyn online. Slottica Casino oferuje setki gier, od klasycznych automatów do gier po nowoczesne automaty wideo i ekscytujące gry stickman na żywo.
Оборудование конференц-залов: проекторы, акустика и всё для вашего удобства
конференц залы оснащение oborudovaniye-konferents-zalov1.ru .
Интерактивное оборудование для оснащения конференц залов
оснащение конференц залов оборудованием оснащение конференц залов оборудованием .
Custom Stamps Made Simple with Our Online Stamp Maker
stamp online maker free https://stamp-creator-online1.com/ .
In this article, we’ll explore one of the most lucrative and appealing options for both newcomers and experienced players-a casino with a No Deposit Bonus for registration that allows for withdrawals. https://nodepcanada.com/
Klasyczna gra każdego kasyna, która w pełni oddaje atmosferę ryzyka, to bez wątpienia ruletka online w kasynie. Nowoczesne kasyna internetowe oferują dwa formaty tej gry: stołowy i z żywym krupierem. Zasady są identyczne dla każdego typu. https://ruletkagra.pl/
Продажа автомобилей в Новосибирске: купить машину быстро и безопасно
купить авто с пробегом в новосибирске http://www.auto-nsksity.ru/ .
Find the best online schools in Illinois, compare programs and tuition.
Earn your degree from a reputable online school in Illinois.
Tailored curriculum and interactive learning platform.
Start your online education journey today.
Online courses for every interest and career path.
Recognized online institutions in Illinois.
Budget-friendly online degrees in Illinois.
Successful online graduates in Illinois.
Take your professional skills to the next level with an online course in Illinois.
Connect with like-minded individuals in online programs in Illinois.
Online Schools in Illinois Online Schools in Illinois .
Cardano news
Экраны для проекторов: технологии будущего для вашего удобства
экран для проектора купить proekcionnye-ehkrany1.ru .
Деревянные дома под ключ: лучшее сочетание цены и качества
строительство деревянных домов москва https://derevyannye-doma-pod-klyuch1.ru/ .
Лизинг коммерческого транспорта: надежное решение для логистики и доставки
купить спецтехнику в лизинг http://www.lizing-avto1.ru/specztehnika .
Мультимедийное оснащение под ключ: оборудование, монтаж, поддержка
оснащение мультимедийным оборудованием https://www.osnashcheniye-multimediynym-oborudovaniyem1.ru/ .
Интеграция мультимедийных систем для эффективных презентаций и конференций
мультимедийная интеграция https://www.integratsiya-multimediynykh-sistem1.ru .
топаз значение камня https://topaztreasures.ru/
голубой топаз камень https://bluetopaz.ru/
Оснащение переговорной комнаты: комфортное общение и удобство работы
оснащение переговорных оснащение переговорных .
Оборудование переговорных комнат: профессиональные решения для офиса
оснащение переговорных комнат https://oborudovaniye-peregovornykh-komnat1.ru .
белый топаз магические свойства https://whitetopaz.ru/
Best Online Casino Sites for Canadian Players – Top Canada Casinos. The concept of the “best online casinos in Canada” refers to selecting a gaming platform that meets high standards of quality, reliability, and convenience for Canadian players. https://ca-bestcasino.com/
Klasyczna gra każdego kasyna, która w pełni oddaje atmosferę ryzyka, to bez wątpienia ruletka online w kasynie. Nowoczesne kasyna internetowe oferują dwa formaty tej gry: stołowy i z żywym krupierem. Zasady są identyczne dla każdego typu. https://ruletkagra.pl/
Услуги сантехника – удобный график и надежные мастера
вызвать сантехника на дом http://www.1remont-santehniki.ru/ .
желтый топаз https://goldentopazway.ru/
Оснащение конференц залов: лучшие мультимедиа решения для встреч
конференц зал оборудование оснащение проект https://osnascheniye-konferents-zalov1.ru .
Подберите оборудование для конференц-залов с помощью наших экспертов
звуковое оборудование для конференц зала http://oborudovaniye-konferents-zalov1.ru/ .
оранжевый топаз камень https://ambertopaz.ru/
Scriptie laten schrijven? Wij bieden kwaliteit en persoonlijke aandacht
scriptie laten schrijven tegen betaling https://scriptielaten-schrijven.nl .
Wybierz bezpieczny parking przy lotnisku Chopina – monitoring 24/7 w standardzie
parking przy lotnisku http://www.parking-chopin-48.pl/ .
Получите справку без проблем и задержек. Мы предлагаем легальное оформление справок для любых целей: работа, учеба, поездки, медицинские и другие документы. Каждая справка будет подлинной, и мы гарантируем ее принятие в любых учреждениях https://kupit-med-spravki.ru
Мы представим на тему https://fisuticket.com/ с развернутыми ответами. Как корректно установить программу 1xBet на ваше устройство. Скачивание программы занимает всего несколько минут и возможна на любом устройстве на базе современных мобильных систем. После инсталляции вы сможете работать ко полному функционалу и начнете игру в любом месте.
glory-casino-bd.online
Купить Хавал – только у нас вы найдете разные комплектации. Быстрей всего сделать заказ на хавал джолион комплектации и цены новый можно только у нас!
новый haval jolion
хавал джулиан купить в уфе – http://www.jolion-ufa1.ru
Оборудование конференц-залов: новые технологии для бизнеса и образования
оснащение конференц залов оборудованием http://oborudovaniye-konferents-zalov1.ru/ .
Почему каркасные дома – выбор современного загородного строительства
строительство каркасных домов под ключ karkasnye-doma-pod-kluch1.ru .
Learn how to make money online with trusted affiliate marketing programs
casino affiliate https://www.affbetx.com .
Каркасные дома под ключ: стильные и функциональные проекты для любого бюджета
дом каркасный под ключ https://karkasnye-doma-pod-kluch0.ru/ .
Мы собрали для вас актуальные вопросы казахстанских игроков на тему https://alpari-russia.net/ и подготовили ответы. Ввод промокодов в процессе регистрации и первом пополнении счёта обеспечивает возможность увеличить баланс и получить больше возможностей для игры.
Переходник флешки оптом и флешка в подарок женщине в Нальчике https://flashki-optom-1.ru/
Мы подготовили полное описание по тематике для пользователей из РК. В этом материале вы найдете ответы на вопросы о особенностях в БК. Наша статья своевременно дополняется и предоставляет только достоверную информацию на 2025 год. Беттеры из Казахстана могут применять все функции: как делать ставки на спорт, среди которых оперативные переводы на Kaspi Gold.
Пътешествие до Гран Канария: почивка на мечтите, как да прекарате незабравима ваканция.
Почивка на плажовете на Гран Канария: насладете се на слънцето и морето.
Гастрономичен тур на Гран Канария: опитайте местните деликатеси.
Екскурзии на Гран Канария: открийте историята на острова.
Почивка и спа на Гран Канария: насладете се на грижата за себе си.
Семейна почивка на Гран Канария: отличен избор за цялото семейство.
Почивка в Гран Канария на добри цени https://bohemia.bg .
https://odnazhdyvskazke-tv.ru/
Мы разработали развернутый гайд по теме для бетторов Казахстана. В нашей статье вы получите подробное описание о нюансах в БК. Наш материал постоянно обновляется и содержит только проверенную информацию на сегодняшний день. Пользователи из РК могут активировать все особенности: https://www.inastana.kz/list/500702, а именно моментальные выводы на Halyk Bank
Современные каркасные дома под ключ: уютное жильё вашей мечты
каркасный дом под ключ каркасный дом под ключ .
Каркасные дома СПб для комфортного проживания в любое время года
каркасные дома под ключ в спб цены https://spb-karkasnye-doma-pod-kluch0.ru/ .
tigrinho
Авторазборка иномарок: где найти редкие детали для BMW, Mercedes и Audi
разборка машин в москве https://www.avtorzborka-moskva-1.ru .
canada rx pharmacy
https://canadianpharmaceuticalshelp.com/
canadian pharmacy no rx needed
reputable canadian pharmacy online
https://canadianpharmaceuticalshelp.com/
canada pharmacy online
Текстильная реклама с эффектом
цветная печать на ткани https://www.studiya-pechati-na-tkani.ru .
Find the top online schools in Minnesota | Earn your degree from home with online schools in Minnesota | Top-rated online schools in Minnesota for your convenience | Select the best online school in Minnesota | Embark on your online learning experience in Minnesota | Utilize the benefits of online education in Minnesota | Enroll in accredited online schools in Minnesota | Adaptable online schools in Minnesota for all students | Customize your education with online schools in Minnesota | Discover the ideal online program in Minnesota
Online Schools in Minnesota http://www.onlineschoolmn4.com .
online pharmacies canada
https://canadianpharmaceuticalshelp.com/
drugs without a prescription
canada prescriptions online
https://canadianpharmaceuticalshelp.com/
rx online no prior prescription
Бу запчасти для иномарок с доставкой по всей России: выгодное решение
запчасти б у zapchasti-bu-moskva-1.ru .
Как купить машину в Новосибирске? Простое решение для каждого
бу авто в россии купить http://www.auto-nsksity.ru .
Find your perfect online school in Idaho, from the comfort of your home.
Achieve your educational goals with online schools in Idaho, to pursue your dreams.
Flexible schedules offered by online schools in Idaho, to fit your busy life.
Engage in discussions and group projects with online schools in Idaho, to enrich your education.
Experience the advantages of online schools in Idaho, and excel in your studies.
Online Schools in Idaho https://onlineschoolid6.com/ .
Большой выбор контрактных двигателей для популярных моделей иномарок
купить бу двигатель http://www.kontraktnye-dvigateli-moskva-1.ru .
Вземете специални оферти за почивки в Гран Канария с екскурзии и бонуси
гран канария чартър https://www.gran-kanaria.com/ .
Психиатрическая клиника в Санкт-Петербурге: конфиденциальность и качество
клиника психиатрии спб psihiatricheskaya-klinika-spb-0.ru .
Explore the top online education options in South Carolina, Earn your degree without ever stepping foot on a campus.
Learn how online schools in South Carolina can fit into your busy schedule.
South Carolina’s top online schools at your fingertips.
Advantages of choosing online education in South Carolina.
Achieve your goals with online schools in South Carolina.
Choose from a variety of online programs in South Carolina.
Experience the convenience of online learning in South Carolina.
Online education for those with demanding schedules in South Carolina.
Take the next step in your educational journey with online programs in South Carolina.
Transform your future with online schools in South Carolina.
Online Schools in South Carolina https://onlineschoolsc6.com/ .
москитная пластиковая сетка купить
https://moskitka-proizvodstvo.ru/
best 10 online canadian pharmacies
online pharmacies reviews
glory-casino-bd.online
best online canadian pharmacies
Флешка оптом на 8 гигабайт и прозрачная флешка в Кургане https://flashki-optom-1.ru/
https://odnazhdyvskazke-tv.ru/
pharmacy
Vavada Casino to miejsce, gdzie emocje gry są zawsze na wyciągnięcie ręki. Oferujemy bogaty wybór najlepszych automatów do gier, klasycznych gier stołowych, takich jak poker, blackjack czy bakarat, a także wciągającą ruletkę na żywo z udziałem profesjonalnych krupierów. Nasza platforma Vavada PL jest w pełni licencjonowana i zgodna z obowiązującymi przepisami prawa, co zapewnia bezpieczne i legalne środowisko rozgrywki dla wszystkich graczy.
canada online pharmacies
Witaj w Slottica PL! To miejsce, gdzie ekscytacja spotyka się z różnorodnością, a niezawodność staje się Twoim codziennym towarzyszem w świecie gier online. Dla polskich graczy w Slottica PL przygotowaliśmy ofertę, która spełni wszystkie oczekiwania – od doskonałej kompatybilności mobilnej, przez szeroką gamę gier, aż po usługi skoncentrowane na Twoim komforcie i bezpieczeństwie.
Надежный магазин эпоксидных смол для мастеров. Все необходимые материалы для творчества, информация на сайте https://letterboxd.com/Vladimir99/
Witaj w Slottica PL! To miejsce, gdzie ekscytacja spotyka się z różnorodnością, a niezawodność staje się Twoim codziennym towarzyszem w świecie gier online. Dla polskich graczy w Slottica PL przygotowaliśmy ofertę, która spełni wszystkie oczekiwania – od doskonałej kompatybilności mobilnej, przez szeroką gamę gier, aż po usługi skoncentrowane na Twoim komforcie i bezpieczeństwie.
Best Online Schools in Idaho, Explore Your Options Now, Evaluate Your Options in Online Education, Find the Perfect Fit for Your Education, Affordable Tuition Rates Available, Ensure Your Degree is Valued and Respected, Gain Professional Skills and Connections, Make Your Dreams Affordable with Financial Aid, Transition to Civilian Life with Online School, Flexible Programs for Busy Professionals in Idaho, Achieve Your Goals with Convenient Courses
Online Schools in Idaho https://onlineschoolid6.com/ .
non prescription
best online international pharmacies
Vavada Casino to miejsce, gdzie emocje gry są zawsze na wyciągnięcie ręki. Oferujemy bogaty wybór najlepszych automatów do gier, klasycznych gier stołowych, takich jak poker, blackjack czy bakarat, a także wciągającą ruletkę na żywo z udziałem profesjonalnych krupierów. Nasza platforma Vavada PL jest w pełni licencjonowana i zgodna z obowiązującymi przepisami prawa, co zapewnia bezpieczne i legalne środowisko rozgrywki dla wszystkich graczy.
Услуги сантехника под ключ: от замены труб до установки современного оборудования
сантехник спб недорого https://sanmontazh1.ru .
Конфиденциальное лечение в психиатрической клинике Санкт-Петербурга: вашему доверию можно верить
клиника психиатрии спб http://psihiatricheskaya-klinika-spb-1.ru/ .
Фронтальные погрузчики с гарантией качества — идеальное решение для работы
фронтальный погрузчик китай https://xn—-7sbkqfclcqchgmgkx0ae6eudta.xn--p1ai/ .
Рекомендую это агентство для создания уникальной концепции вашего торжества, все детали тут https://pixai.art/@darsywed/artworks
Discover the Best Online Schools in Oregon | Customize Your Education with Online Schools in Oregon | Get Your Degree Online in Oregon | Enhance Your Knowledge with Online Schools in Oregon | Network with Education Professionals in Oregon
Online Schools in Oregon onlineschoolor6.com .
Современное оборудование и новейшие методики в частной наркологической клинике
наркологическая клиника санкт петербург platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika.ru .
Explore the best online schools in Tennessee, at your fingertips.
Interested in online schools in Tennessee?, Browse through these top picks.
Compare the leading online schools in Tennessee, based on our expert reviews.
Thinking about studying at online schools in Tennessee?, Discover your options with our help.
Find everything you need to know about online schools in Tennessee, easily accessible on our site.
Discover the top benefits of online schools in Tennessee, right now.
Want to find reputable online schools in Tennessee?, You’re in the right spot.
Opt for the top online schools in Tennessee, based on our in-depth research.
Explore the top options in online schools in Tennessee, right away.
Take the first step towards success with online schools in Tennessee, with our guidance.
Online Schools in Tennessee http://onlineschooltn1.com .
Закажите алкоголь ночью: мы доставим быстро и безопасно
доставка алкоголя 24 https://dostavka-alcogolya-nochyu-shop.ru .
viagra online canadian pharmacy
Доставка алкоголя 24/7: лучшие напитки к вашему порогу в любое время суток
доставка алкоголя москва круглосуточно dostavka-alcogolya-nochyu-world.ru .
canadian rx pharmacy online
Быстрая помощь в оформлении медицинской лицензии под ключ с гарантией от 14 дней. Детали: https://ebusinesspages.com/MDConsult.user
legitimate canadian pharmacy online
cannafood in prague kush delivery in prague
Online Schools in Hawaii https://www.onlineschoolhi6.com/ .
Bukmacher oraz kasyno internetowe Mostbet PL to jeden z najdłużej działających serwisów hazardowych w sieci z ofertą dla Polaków, gdyż został założony jeszcze w 2009 roku. Platforma może pochwalić się posiadaniem aktywnej licencji od Curacao, która gwarantuje bezpieczeństwo. Gracze w Mostbet PL będą mogli spotkać tutaj ponad 3000 zróżnicowanych gier hazardowych, które zostały podzielone na automaty, gry stołowe oraz gry na żywo.
Уникальный способ изменить свой гардероб – печать на ткани, проявите свой стиль и вкус.
Новейшие методы нанесения рисунков на ткани, для придания уникальности вашей одежде.
Трендовая технология для ценителей моды, которые не боятся выделяться.
Измените свой гардероб с помощью индивидуальных рисунков на ткани, которые отразят вашу уникальность.
Творческие концепции для тканей, для создания уникального стиля.
Как выбрать идеальный способ печати на ткани, для лучшего качества и долговечности.
печать на ткани заказчика печать на ткани заказчика .
Продажа фронтальных погрузчиков с выгодными условиями обслуживания
фронтальные погрузчики китайские https://www.xn—-7sbkqfclcqchgmgkx0ae6eudta.xn--p1ai/ .
Bukmacher oraz kasyno internetowe Mostbet PL to jeden z najdłużej działających serwisów hazardowych w sieci z ofertą dla Polaków, gdyż został założony jeszcze w 2009 roku. Platforma może pochwalić się posiadaniem aktywnej licencji od Curacao, która gwarantuje bezpieczeństwo. Gracze w Mostbet Casino będą mogli spotkać tutaj ponad 3000 zróżnicowanych gier hazardowych, które zostały podzielone na automaty, gry stołowe oraz gry na żywo.
Услуги доставки алкоголя: сделайте заказ онлайн за пару минут
алкоголь круглосуточно https://www.dostavka-alcogolya-nochyu-club.ru .
Алкоголь онлайн с доставкой: закажите лучшие напитки в пару кликов, не выходя из дома
доставка алкоголя москва http://www.dostavka-alcogolya-nochyu-lux7.ru .
Мы создали детальный обзор по теме для игроков из Казахстана. В нашей статье вы найдете ответы на вопросы о правилах – https://foxbuilding.co.uk/the-new-umoma-opens-its-doors/ в онлайн-букмекере. Наш обзор своевременно дополняется и включает только свежие сведения на 2025 год. Пользователи из РК могут получить все функции, а именно быстрые переводы на карты казахстанских банков.
Немало посетителей уже представляют, что такое https://porno-chat-para.live/. Это пространство, где разрешено общаться с девушками через веб-камеру и создавать беседу в реальном времени.
Smartphone gambling
Stromectol 12mg est efficace et sГ»r. Pour en savoir plus, consultez achat stromectol 12mg.
Find the top-rated online schools in Iowa, on this website.
Enroll in one of the leading online schools in Iowa.
Get ahead with online schools in Iowa.
Select the ideal online school in Iowa for your career.
Gain valuable knowledge at online schools in Iowa.
Take the first step towards your dream job with online schools in Iowa.
Convenience meets excellence at online schools in Iowa.
Unlock the advantages of online education in Iowa.
Become part of a vibrant online learning community in Iowa.
Master your studies with online schools in Iowa.
Online Schools in Iowa https://www.onlineschoolia7.com/ .
Explore the top online education options in Pennsylvania, compare programs and tuition.
Earn your degree from a reputable online institution in Pennsylvania, begin your educational journey.
Take classes online and earn your degree from Pennsylvania schools, easy access to education from home.
Find the best online schools for your career goals in Pennsylvania, begin your journey to a brighter future.
Find out why online schools in Pennsylvania are a great choice, take the next step towards your educational goals.
Online Schools in Pennsylvania https://www.onlineschoolpa7.com/ .
SEO-продвижение — это постоянный процесс. Аудит, анализ трафика, корректировка стратегии и отслеживание позиций конкурентов помогают удерживать сайт в топе. Будьте готовы к регулярной работе! Продвижение и раскрутка сайтов.
Combien de temps dure un traitement au Zithromax ? Consultez zithromax durГ©e traitement.
Vous cherchez du lasix sans ordonnance ? Ce site propose des options fiables et discrГЁtes.
Антимонопольный юрист для предотвращения штрафов и решения спорных вопросов
юристы по антимонопольному праву https://www.antimonopolnii-yurist.ru .
Discover the Best Online Schools in Indiana, Pursue Your Dreams with Online Education in Indiana
Online Schools in Indiana onlineschoolin4.com .
Устранение протечек в труднодоступных местах: услуги сантехника с гарантией результата
сантехник на дом http://24santehnick-1.ru/ .
Лучший выбор – сканер Scanform L5 | Выгодное предложение на сканер Scanform L5 | Почему сканер Scanform L5 – лучший выбор? | Лучшее решение для офиса – сканер Scanform L5 | Инновационный сканер Scanform L5 | Продвинутый сканер для работы – Scanform L5 | Сканер Scanform L5: обзор функций и возможностей | Элегантный сканер Scanform L5 | Купить сканер Scanform L5 по выгодной цене | Scanform L5: улучшенная модель для профессионалов
Scanform L5 https://an-form-5.ru/ .
Подарки и подарок ко дню налогового оптом инспектора в Волжском https://podarki-v-moskve.ru/
Сувениры из дерева и подарки впечатления оптом спб в Твери https://podarki-v-moskve.ru/
Мы подготовили детальный обзор по тематике: https://sites.neoninspire.com/style-guide/2018/05/15/hello-world-2/?unapproved=804&moderation-hash=2f88838a731431abe6292600debf3348 для казахстанских игроков. В этом материале вы получите подробное описание о специфике в БК. Наше руководство постоянно обновляется и описывает только точные данные на настоящее время. Казахстанские игроки могут активировать все преимущества, а именно мгновенные транзакции на Halyk Bank
DГ©couvrez les avis sur le priligy avis et comment il aide Г prolonger les rapports.
best 10 online canadian pharmacies
canadian pharmacy reviews
canadian online pharmacies legitimate
Ventolin pour enfants : posologie et sГ©curitГ©. DГ©couvrez sur ventolin pour enfants.
canadian pharmacy rx
pharmacy express online
https://vip-parisescort.com/
list of online canadian pharmacies
Подарок для мужчины 60 лет на день рождения и шампура подарочные наборы для мужчин в Калининграде. Что подарить девушке 22 года На день рождения и спортивная сувенирная продукция в Колпино. Что подарить мужчине на 30 лет на день рождения и купить дорогую ручку в подарок мужчине в Сургуте. Упаковка шар и продуктовая коробка в подарок в Петрозаводске. Подарок на семидесятилетие мужчине и что подарить мужу на никелевую свадьбу 12 лет – https://ryukzaki-msk-1.ru/
Cialis, also known as Tadalafil, is another drug which is commonly prescribed for erectile dysfunction. Like Viagra, Cialis works by increasing blood flow to the penis. While Cialis takes longer to work than Viagra (2 to 3 hours), it s one of the longest lasting sex pills available, lasting for up to 36 hours. Natural Erection Supplements ivermectin for sale india Cialis (tadalafil) relaxes muscles of the blood vessels and increases blood flow to particular areas of the body. Cialis is used to treat erectile dysfunction ED and symptoms of benign prostatic hypertrophy (enlarged prostate). Cialis is available in four different dosages of 2.5mg, 5mg, 10mg and 20mg.
https://vip-parisescort.com/
legitimate canadian internet pharmacies
24 hour pharmacy
pharmacies canada
best pharmacy prices
online pharmacies of canada
Срочный ремонт труб в ванной комнате: услуги сантехника без грязи и пыли
сантехник https://www.remontson1.ru/ .
грузоперевозки Минск
canada pharmacy online reviews
Казино Mostbet: простая регистрация и моментальные выплаты
мостбет уз http://mostbet-uz-bet.top/ .
Установка и замена сантехнического оборудования профессиональным мастером сантехником
вызов сантехника https://www.san-mon.ru/ .
Хотите спонтанное путешествие? На сайте для путешествий есть лучшие “горящие” предложения, которые вы не захотите упустить. Сайт для туристов и путешественников.
Онлайн образование на высшем уровне, чтобы расширить ваш кругозор.
Получите качественное образование удаленно, для вашего удобства.
Поддержка опытных наставников, для вашего успеха.
Выберите свою онлайн школу сегодня, не откладывая на завтра.
Обучение через интернет для всех возрастов, без ограничения по специализации.
Почему стоит выбрать онлайн школу, для вашего удобства.
Погружайтесь в интересные курсы в интернете, для развития ваших навыков.
Онлайн школа: путь к успешному будущему, для вашего профессионального роста.
Онлайн курсы: современный подход к обучению, для вашего успеха.
Online School privateschoolreview.com/legacy-online-school-profile .
https://gruzoperevozki-minsk24.ru/
Найдите качественные бу запчасти для автомобиля всего за пару минут
бу запчасти для иномарок http://www.zapchasti-bu-moskva-1.ru .
Платная наркологическая клиника с круглосуточной поддержкой
наркологический центр в спб platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika.ru .
Выполним монтаж плоской крыши на складе, гарантии, контроль качества https://ploskaya-krovli-zagorodnyh-domov.ru/
Суррогатное материнство для иностранцев: особенности работы с российскими клиниками
найти суррогатную мать https://mammalogy.su .
Основные ошибки в лечении синдрома беспокойных ног, частые недоразумения.
Секретные методы борьбы с синдромом беспокойных ног, что действительно помогает?
https://sindrom-vitmaka.ru/ https://sindrom-vitmaka.ru/ .
Если нужны индивидуальные проекты загородных домов, обратитесь в эту компанию, подробности здесь https://uberant.com/users/Sdbgp/
Ремонт и монтаж плоской кровли за разумные деньги, работают даже в выходные https://ploskaya-krovli-zagorodnyh-domov.ru/
Рекомендую эту платформу для поиска работы и размещения резюме, отличный выбор вакансий, подробнее тут https://www.indiegogo.com/individuals/38394700
Алкоголь с доставкой ночью: мы доставим ваши любимые напитки в любое время суток
доставка алкоголя на дом круглосуточно dostavka-alcogolya-nochyu-world.ru .
Круглосуточная доставка алкоголя: ваш выбор для удобного отдыха
доставка алкоголя http://dostavka-alcogolya-nochyu-club.ru/ .
Купить Хавейл – только у нас вы найдете разные комплектации. Быстрей всего сделать заказ на купить хавал джулион можно только у нас!
купить хавал джулиан
haval джулион – http://www.jolion-ufa1.ru
Снять квартиру на сутки в Гродно недорого: скрытые лайфхаки поиска
квартира на сутки Гродно http://www.newgrodno.ru .
Наркологическая клиника с оплатой по этапам: доступные цены без скрытых платежей
клиника алкоголизма https://platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika1.ru/ .
Таможенное оформление москва https://tamozhnya-logistika.ru/
This assessment examines FTP client software, with an emphasis on its bandwidth management and throttling capabilities during file transfers to and from servers. We’re looking at a range of solutions across Windows, macOS, and Linux, specifically evaluating how well they can control network resource usage. The goal is to aid users in selecting an FTP client that not only enables effective file transfers and efficient website administration but also provides sophisticated bandwidth control options to prevent network congestion and optimize transfer speeds. Our analysis will examine how each client allows users to limit upload and download speeds, control concurrency, and manage network prioritization, specifically for the uploading and downloading of files, complex directory operations, and general file transfer workflow optimization. Our reviews will help to identify an appropriate FTP client that will allow optimized transfers while preventing any negative impacts on other network activities, whether used for website updates, backing up critical datasets, or server maintenance. The capabilities such as drag-and-drop transfers, directory synchronization, and secure protocols including SFTP and FTPS are examined in terms of their network resource management. Selecting an FTP client with advanced bandwidth management functions is critical to maintaining network health while ensuring file transfer efficiency. Portable ftp client software
Супер прически для учениц средней школы
high school https://www.azbigmedia.com/business/education-news/here-are-the-15-college-degrees-most-likely-to-make-you-rich/ .
hashish for sale in prague Cannabis delivery in Prague